CSS
What is CSS?
CSS is the language we use to style an HTML document, CSS describes how HTML elements should be displayed.
What is CSS exactly for?
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML. … CSS is designed to enable the separation of presentation and content, including layout, colors, and fonts.
** CSS-syntax **
A CSS rule consists of a selector and a declaration block.
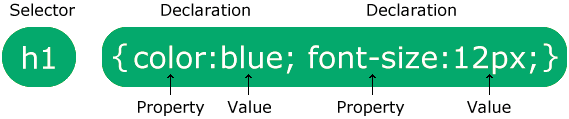
 
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
Example:
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
Example Explained
- p is a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).
- color is a property, and red is the property value
- text-align is a property, and center is the property value
How To Add CSS
When a browser reads a style sheet, it will format the HTML document according to the information in the style sheet.
Three Ways to Insert CSS
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
External CSS
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the element, inside the head section.
Internal CSS
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the
Inline CSS
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
** Cascading Order**
What style will be used when there is more than one style specified for an HTML element?
All the styles in a page will “cascade” into a new “virtual” style sheet by the following rules, where number one has the highest priority:
- Inline style (inside an HTML element)
- External and internal style sheets (in the head section)
- Browser default
So, an inline style has the highest priority, and will override external and internal styles and browser defaults.
CSS color Property
Definition and Usage
The color property specifies the color of text.
The color CSS property sets the foreground color value of an element’s text and text decorations, and sets the
Tip: Use a background color combined with a text color that makes the text easy to read.
colors Syntax
/* Keyword values */
color: currentcolor;
/* <named-color> values */
color: red;
color: orange;
color: tan;
color: rebeccapurple;
/* <hex-color> values */
color: #090;
color: #009900;
color: #090a;
color: #009900aa;
/* <rgb()> values */
color: rgb(34, 12, 64, 0.6);
color: rgba(34, 12, 64, 0.6);
color: rgb(34 12 64 / 0.6);
color: rgb(34.0 12 64 / 60%);
color: rgba(34.6 12 64 / 30%);
/* <hsl()> values */
color: hsl(30, 100%, 50%, 0.6);
color: hsla(30, 100%, 50%, 0.6);
color: hsl(30 100% 50% / 0.6);
color: hsla(30 100% 50% / 0.6);
color: hsl(30.0 100% 50% / 60%);
color: hsla(30.2 100% 50% / 60%);
/* Global values */
color: inherit;
color: initial;
color: unset;
The color property is specified as a single
Note that the value must be a uniform color. It can’t be a